Quant Trading
Quantitative trading, also known as quant trading, is a complex and sophisticated field of quantitative finance that uses mathematical and statistical models to identify profitable trading opportunities. This article will explore the origins, key concepts, and advantages and disadvantages, providing readers with a comprehensive understanding of this fascinating field.
What Is Quant Trading?
Quantitative trading is a market strategy that utilizes mathematical and statistical models to identify trading opportunities and act on them in a timely manner. The name “quantitative” comes from the fact that data-driven analysis is what drives the models.
For instance, a trader interested in momentum or trend trading may develop or purchase software that uses specific parameters to select stocks based on a rising market trend. The program would then automatically buy stocks based on those parameters and track the market’s upward trend, allowing the trader to take advantage of potential profits.
How Does Quant Trading Work?
Quantitative traders are well-versed in using numerical tools such as moving averages, which form clever trading techniques when combined with technology, mathematics, and statistical models. These traders create mathematical models based on their trading strategies by analyzing past data.
In addition, quantitative traders often rely on variables such as price and trading volume to inform their trading approaches. Although share price changes can be unpredictable and cyclical, these quantitative tools can help traders capitalize on those trends.
The strategies developed by quantitative traders are ultimately put to use in the market, with actual funds at stake. These models are similar to climate forecasting, which uses probabilistic methods based on past weather data to make predictions.
What Is A Quant Trader?
Quantitative traders are specialized traders who utilize quantitative and statistical techniques to evaluate financial instruments and markets. By doing so, they can identify potential trading opportunities and assess the associated risks.
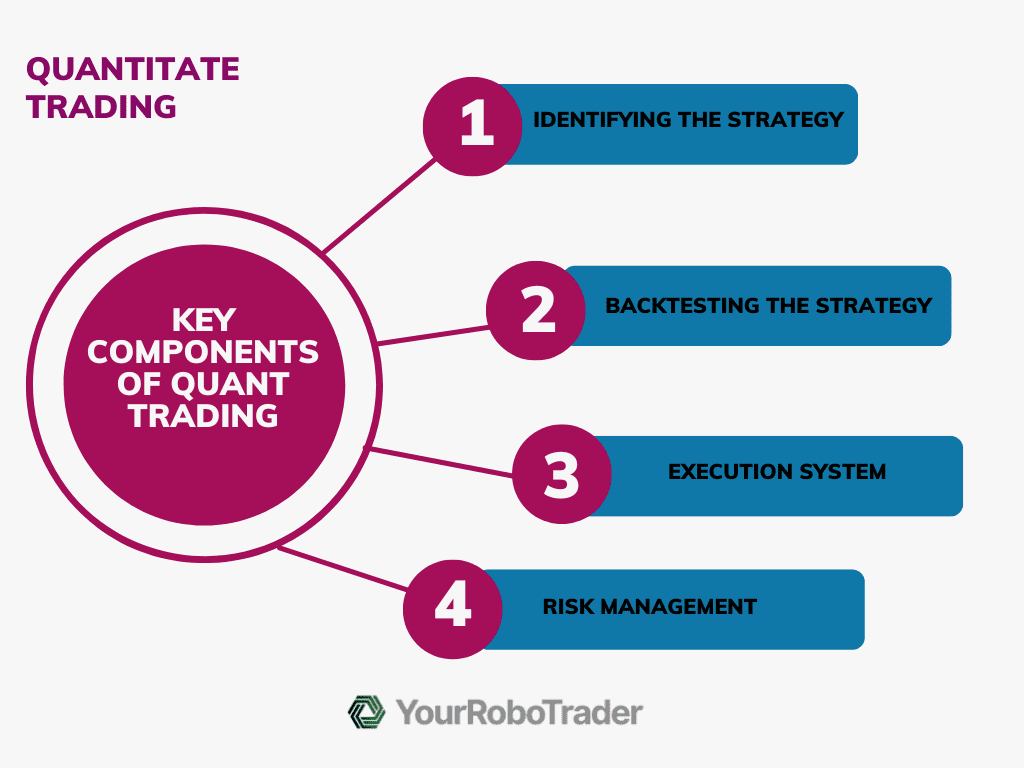
Key Components Of Quant Trading
There are four key parts to every quantitative trading system, which include:
Identifying the Strategy
The first step in the quantitative trading process is research, which is choosing a trading strategy and determining whether it is consistent with other trader techniques.
Backtesting the Strategy
Understanding if the strategy determined in the first phase is lucrative when used with historical and out-of-sample data is the aim of strategy backtesting.
Execution System
The interface to the brokerage, lower transaction costs, and performance divergence between the live system and the backtested performance are the main factors to be considered while developing an execution system.
Risk Management
Risk management is a critical factor to consider. This includes potential biases such as technology risk and brokerage risk, which refers to the risk of broker bankruptcies.
Quantitative vs Algorithmic Trading
When it comes down to it, algorithmic trading essentially consists of a set of rules based on previous data that traders use to enter and exit positions in the future to maximize profit. Quantitative trading involves predicting future market trades using statistics, mathematical models, and large datasets.
Quantitative trading makes use of mathematical and statistical models to forecast market patterns. On the other hand, algo trading makes an effort to profit from changes in the market by executing trades automatically following predefined criteria.
Both algorithmic and quantitative trading use computers to automate the trading process. Still, they take very different approaches regarding the kinds of trading instruments they use and how they are used.
Quantitative Trading vs Algorithmic Trading
| Quantitative Trading | Algorithmic Trading | |
|---|---|---|
| Approach | Predicts future trades using mathematical and statistical models | Maximizes profit by executing trades automatically based on predefined rules and data |
| Tools used | Large datasets, statistical models, mathematical algorithms | Historical data, technical indicators, predefined rules |
| Goal | Forecast market patterns | Profit from market changes |
| Trading instruments | Can be applied to a wide range of trading instruments | Mainly used for high-volume trading instruments such as stocks, options, and futures |
| Human input | Involves human input for developing and refining models | Fully automated, no human input required |
| Timeframe | Can operate on a range of timeframes | Often operates on short timeframes, such as milliseconds or microseconds |
| Risks | Involves risk management to address potential biases and risks | May be subject to errors or glitches in software or data processing |
| Popularity | Widely used by institutional investors and hedge funds | Increasingly used by individual traders as well as institutional investors |
Advantages Of Quant Trading
Improved accuracy and efficiency
Quantitative approaches to trading utilize computer algorithms to analyze and make effective trading decisions, which can lead to increased efficiency. By removing the influence of emotions such as fear and greed, these approaches enable traders to make more objective and rational decisions. Ultimately, this can lead to better trading outcomes.
Objective decision making
A variety of circumstances influence the choices that traders make during trading. However, when traders employ a quantitative trading strategy, choices are made purely based on data and statistics. This can reduce the potential for emotional trading decision-making, promote objective trading decision-making, and result in more profitable trades.
Risk management
The term “risk” in trading encompasses numerous potential sources of interference with trade implementation, which can be numerous. This includes technological risks, such as the possibility of co-located exchange servers unexpectedly experiencing a hard disk issue, as well as the risk of broker bankruptcies. In short, it covers almost all potential obstacles that may hinder trade execution.
Disadvantages In Quant Trading
Data quality and availability
Quantitative trading offers superior returns for those relying on mathematical and statistical models. Investors should ensure that the strategies they are building are updated following the current market occurrences, as quantitative trading can involve techniques and models that may over-rely on data and neglect real-time market unpredictability.
Model overfitting
When testing trading systems, algorithmic traders frequently struggle with overfitting (also known as curve fitting). If traders are not cautious, they risk developing a trading technique that perfectly matches historical data but cannot be used appropriately in practice.
Market volatility
Quantitative trading models must be dynamic to operate successfully in volatile environments like financial markets. In the end, many quantitative traders struggle to adapt to shifting market conditions because they create only temporarily profitable models.
The Future Of Quant Trading
Emerging technologies and their impact
Emerging technologies are having a significant impact on quant trading. In today’s fast-paced trading environment, transactions are executed in microseconds, nanoseconds, and milliseconds, with each millisecond accounting for millions of dollars in annual market trade revenue. The use of technology enables traders to instantly analyze and respond to market events happening around the world, making geography less relevant in the field of trading. This has helped to level the playing field, allowing traders to make more informed and profitable decisions.
Regulatory considerations and the future
The future of quant trading is closely tied to regulatory concerns, as regulations are implemented to safeguard the market and eliminate any potential risks. To achieve this, regulators must understand how algorithms work and be flexible enough to enact new legislation when necessary.
The openness and accountability brought about by algorithmic trading and high-frequency trading (HFT) have led to recent legislative reforms and improvements in Europe, encouraging automation. This, in turn, has paved the way for the expansion and progression of quant trading.
The potential for wider adoption
Quant trading has many valuable characteristics that make it an attractive option for wider adoption. In addition to its simplicity, adaptability, and speed, quant trading is also known for executing trading commands instantly and precisely, thanks to its lack of human emotions and low tolerance for delay. This makes it a highly efficient and effective tool for trading.
Conclusion
In conclusion, quantitative trading has revolutionized the trading industry by utilizing computer algorithms and mathematical models to identify and capitalize on trading opportunities. Analyzing historical data allows quant traders to make informed decisions based on patterns and trends. The advantages of quantitative trading, such as speed, accuracy, and adaptability, have made it a popular approach for high-frequency, algorithmic, arbitrage, and automated trading in both individual and institutional settings. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect quant trading to become even more sophisticated and widely adopted in the future.




